// Databricks notebook source exported at Tue, 28 Jun 2016 11:12:33 UTC
Scalable Data Science
Change Detection in Degree Corrected Stochastic BlockModel Graphs
Scalable data science project by Shakira Suwan
The html source url of this databricks notebook and its recorded Uji  :
:
Network Analysis

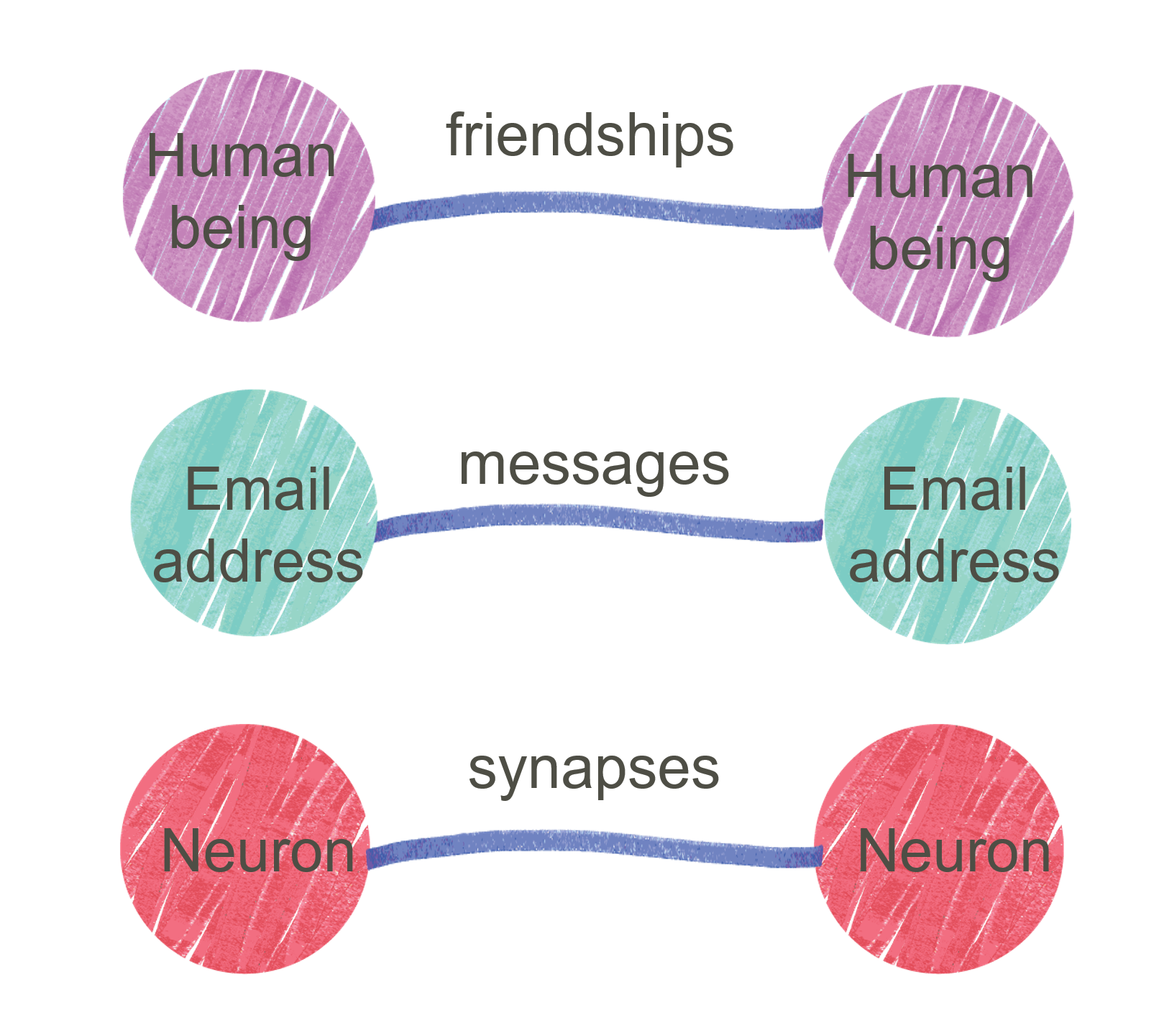
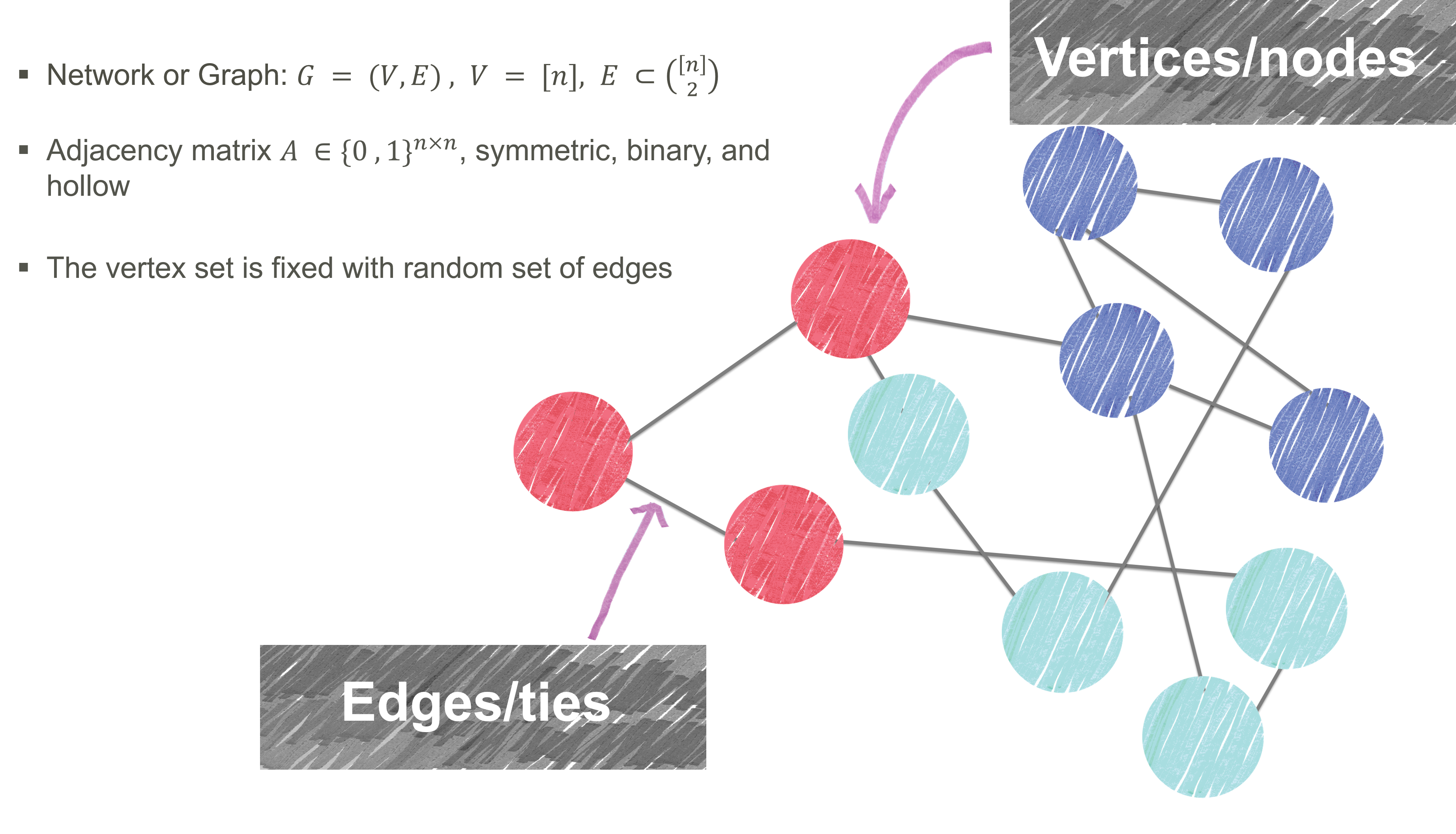
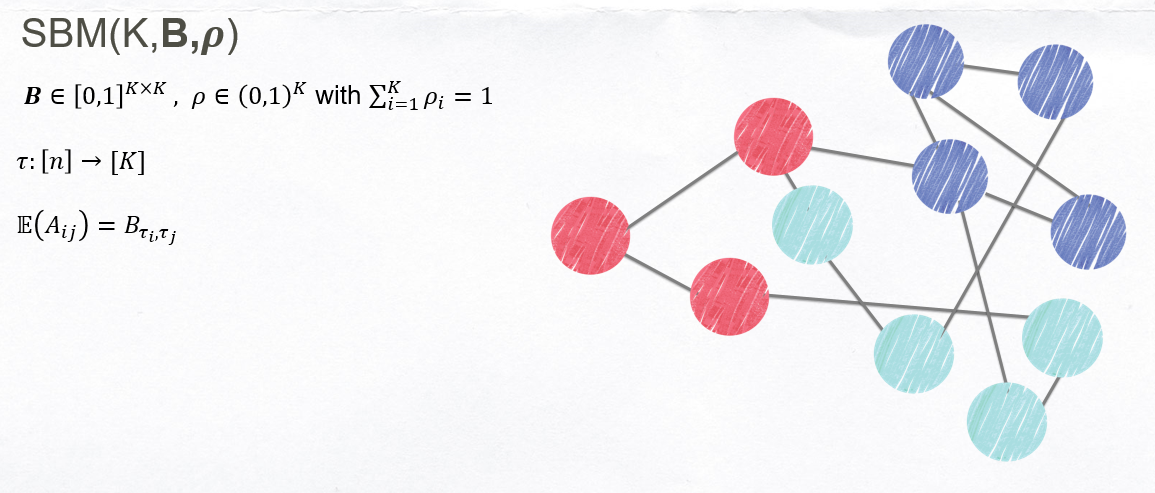
Stochastic Blockmodel
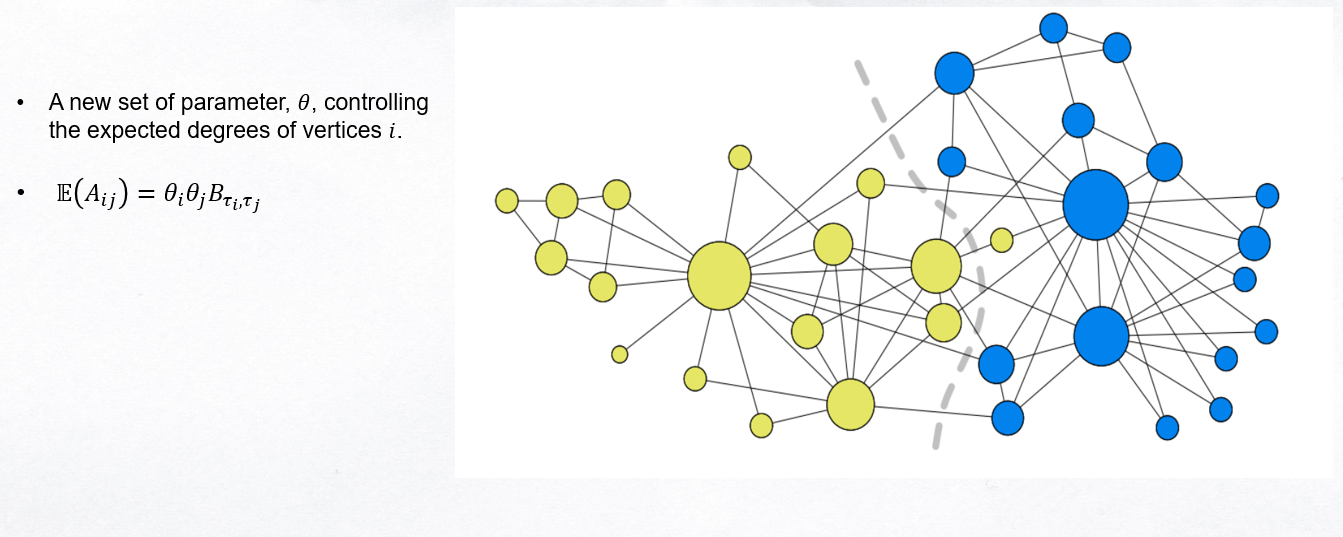
####Limitations:
- SBM treats all nodes within a community as stochastically equivalent.
- Thus does not allow for the existence of “hubs,” high-degree nodes at the center of many communities observed in real data.
- To address this issue, Karrer and Newman [20] proposed the degree-corrected stochastic block model, which can accommodate hubs.
Degree Corrected Stochastic Blockmodel
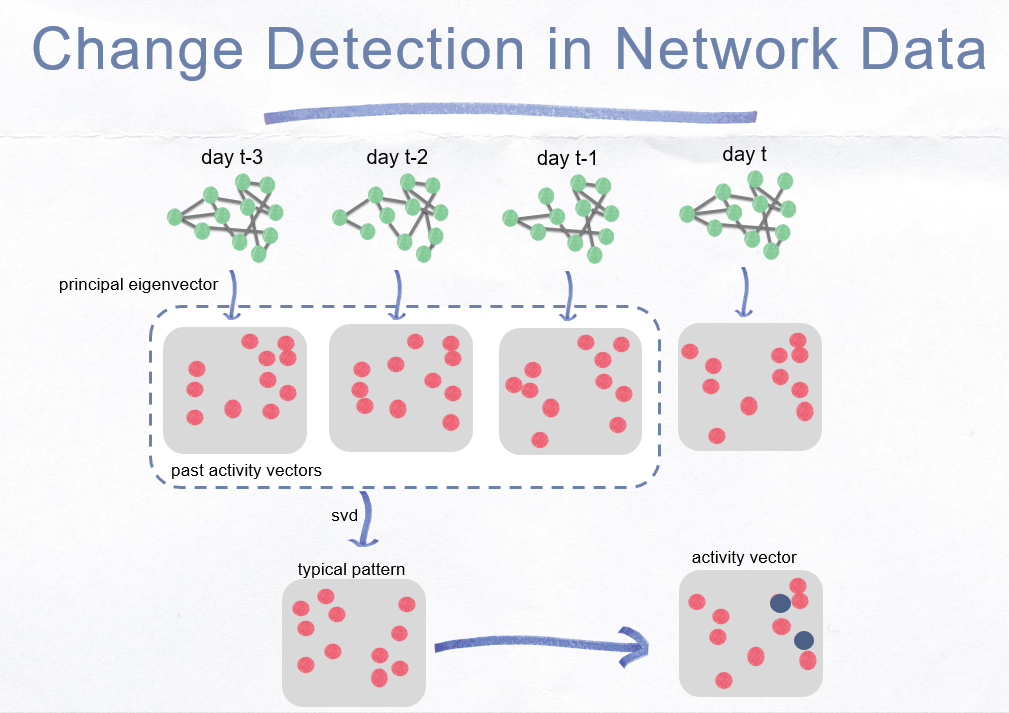
####Change Detection Ide and Kashima (2004) compare the current activity vector with the past average vector (profile vector) by computing the change score \(s_t\) for time instant, \(t\) as
\[s_{t} = 1 - \tilde{\mathbf{u}}(t-1) \cdot \mathbf{u}(t)\]The change scores of the nodes, \(s^i_t\) at time \(t\) is
\[s^i_{t} = \left | \tilde{\mathbf{u}}(t-1) - \mathbf{u}(t) \right |\]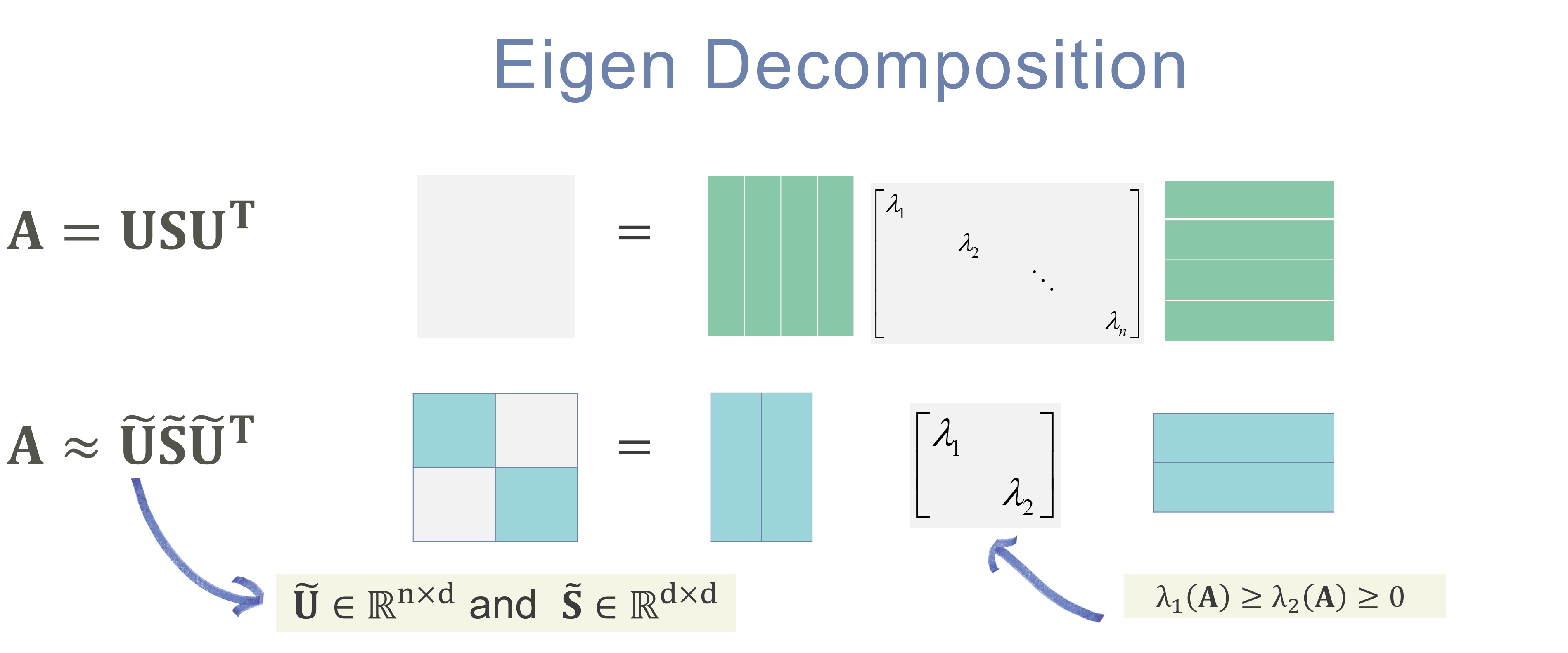
Simulation Studies
####Parameter Setting:
- K =3,
- n= 900
- \(B_{i,i} = 0.05\), for \(i= 1,...,K\)
- \(B_{i,j} = 0.008\), for \(i\neq j\)
- 30 graph realizations
- G =21 is generated from one of the following change scenarios
####Change scenarios:
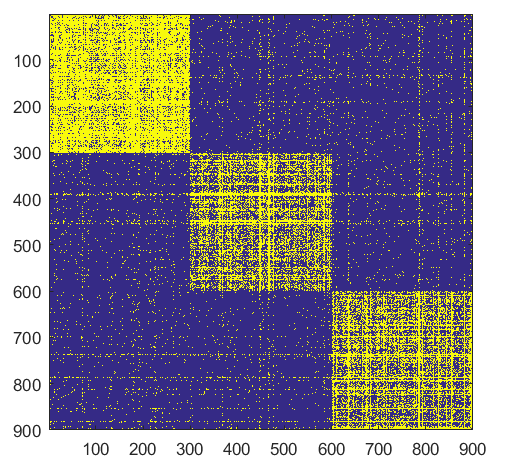
- ####Split
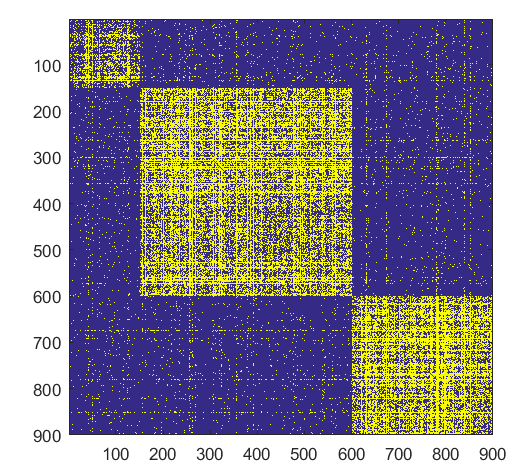
- ####Form
- ####Shift
Source Code
First let’s import various libraries.
import breeze.linalg._
import breeze.numerics._
import breeze.stats.distributions._
####Powerlaw Distribution
- This function returns \(n\) random numbers generated from a powerlaw distribution.
def powerlawRnd(n:Int,xmin:Double, alpha:Double ):DenseVector[Double]={
val u=Range(0,n).map(v=>{
var r= new scala.util.Random
r.nextDouble()
}).toArray
val plx=u.map(a=>xmin*pow((1-a),(-1/alpha-1)))
new DenseVector(plx)
}
DCSBM Graphs
- This function returns an \(n_1 \times n_2\) degree corrected stochastic blockmodel graph
def constructGraph(K:Int,p:DenseVector[Double], r:Double, theta1:DenseVector[Double],theta2:DenseVector[Double],lambda:Double,rho:DenseVector[Double],N1:Int,N2:Int):DenseMatrix[Double]={
var n1_block:DenseVector[Double]= rho :* N1.toDouble
n1_block = floor(n1_block)
var n1_ind = DenseMatrix.zeros[Double](K,2)
val tmp = accumulate(n1_block)
n1_ind(::,1) := tmp -1.toDouble
n1_ind(0,0) = 0;
n1_ind(1 to -1,0) := tmp(0 to -1-1)
var n2_block:DenseVector[Double]= rho :* N2.toDouble
n2_block = floor(n2_block)
var n2_ind = DenseMatrix.zeros[Double](K,2)
val tmp2 = accumulate(n2_block)
n2_ind(::,1) := tmp2 - 1.toDouble
n2_ind(0,0) = 0;
n2_ind(1 to -1,0) := tmp2(0 to -1-1)
var temp1 = DenseMatrix.fill(K,K){n1_block(1)}
var temp2 = DenseMatrix.fill(K,K){n2_block(1)}
var expectedNum = temp1 :* temp2
var p2:DenseVector[Double]=null
if(p.length==1){
var p1=p(0)
p2= DenseVector.fill(K){p1}
}else{
p2 = p
}
var p1 = DenseVector.rangeD(1,K+1,1):* p2//clear structure (p1>p2)
var B = (lambda*DenseMatrix.eye[Double](K):* diag(p1)) :* expectedNum :+ ((1-lambda) * DenseMatrix.fill(K,K)(r) :*expectedNum)
// generate node probabilities
var Z1 = DenseMatrix.zeros[Double](N1,K)
var Z2 = DenseMatrix.zeros[Double](N2,K)
var blockDeg1 = DenseVector.zeros[Double](K)
var blockDeg2 = DenseVector.zeros[Double](K)
var rowDeg = DenseVector.zeros[Double](N1)
var colDeg = DenseVector.zeros[Double](N2)
val n1Ind = n1_ind.mapValues(_.toInt)
val n2Ind = n2_ind.mapValues(_.toInt)
for(k <- 0 to K-1){
blockDeg1(k) = sum(theta1.slice(n1Ind(k,0),n1Ind(k,1)))
blockDeg2(k) = sum(theta2.slice(n2Ind(k,0),n2Ind(k,1)))
rowDeg.slice(n1Ind(k,0),n1Ind(k,1)) := theta1.slice(n1Ind(k,0),n1Ind(k,1)) :/ blockDeg1(k)
colDeg.slice(n2Ind(k,0),n1Ind(k,1)) := theta2.slice(n2Ind(k,0),n2Ind(k,1)) :/ blockDeg2(k)
Z1(n1Ind(k,0) to n1Ind(k,1), k) := 1.0;
Z2(n2Ind(k,0) to n2Ind(k,1), k) := 1.0;
}
var nodeProb = diag(rowDeg) * Z1 * B * Z2.t * diag(colDeg)
// create graph realizations
var W = DenseMatrix.zeros[Double](N1,N2)
for(i<-0 to N1-1){
for(j<- i+1 to N2-1){
var poi= Poisson(nodeProb(i,j))
W(i ,j) = poi.draw
}
}
var A = W
for(i<-0 to N1-1){
for(j<- i+1 to N2-1){
if(W(i,j)!=0.0)
A(i ,j) = 1.0
}
}
var A1 = upperTriangular(A) + upperTriangular(A).t
A1
}
Change Scenarios
- This function returns an \(n_1 \times n_2\) changed dcsbm graph.
// create an anomaly graph, form, split, shift
case class graphAnomalyClass(W:DenseMatrix[Double],A1:DenseVector[Double], A2:DenseVector[Double])
def createA_anomaly(K:Int,p:Double, r:Double, theta1:DenseVector[Double],theta2:DenseVector[Double],lambda:Double,rho:DenseVector[Double],changeType:String, graphType:String):graphAnomalyClass={
var N1:Int = theta1.length
var N2:Int = theta2.length
val s1 = rho(0)*N1.toDouble
val s2 = rho(1)*N2.toDouble
var s1_temp = DenseVector.fill(K){s1}
var s2_temp = DenseVector.fill(K){s2}
val s1_cumsum = accumulate(s1_temp)
var s2_cumsum = accumulate(s2_temp)
val constD = DenseVector{0.0}
val constI = DenseVector{0}
var W_poi:DenseMatrix[Double]=null
var anomalies1:DenseVector[Double]=null
var anomalies2:DenseVector[Double]=null
changeType match{
case "form" =>
var pnew = DenseVector.fill(K)(p)
pnew(0) = pnew(0)*3.0
W_poi = constructGraph(K,pnew,r,theta1,theta2,lambda,rho,N1,N2)
anomalies1 = DenseVector.rangeD(1, s1_cumsum(0)+1,1)
anomalies2 = DenseVector.rangeD(1, s2_cumsum(0)+1,1)
case "split" =>
var stmp1 = DenseVector.vertcat(constD,s1_temp)
var stmp2 = DenseVector.vertcat(constD,s2_temp)
val k2 = K+1
val temp1 = stmp1(1)*0.5
val temp2 = stmp2(1)*0.5
stmp1(0)= temp1
stmp1(1)= stmp1(1) - temp1
stmp2(0)= temp2
stmp2(1)= stmp2(1) - temp2
val rho_tmp = stmp1 :/ N1.toDouble
anomalies1 = DenseVector.rangeD(1,s1_temp(0)+1.0,1)
anomalies2 = DenseVector.rangeD(1,s2_temp(0)+1.0,1)
var pnew = DenseVector.fill(k2){p}
for(i <- 1 to pnew.length-1){
pnew(i) = pnew(i)*(1.0/(i+1.0))
}
var rowV = DenseVector.range(1,k2,1)
rowV = DenseVector.vertcat(constI+1,rowV)
var pnew1 = pnew:*rowV.mapValues(_.toDouble)
W_poi = constructGraph(k2,pnew1,r,theta1,theta2,lambda,rho_tmp,N1,N2)
case "shift" =>
var stmp1 = s1_temp
val temp1 = stmp1(0)*0.5
stmp1(0) = stmp1(0) - temp1
stmp1(1) = stmp1(1) + temp1
var stmp2 = s2_temp
val temp2 = stmp2(0)*0.5
stmp2(0) =stmp2(0) - temp2
stmp2(1) =stmp2(1) + temp2
var rho_tmp = stmp1:/N1.toDouble
var pnew = DenseVector.fill(K){p}
anomalies1 = DenseVector.rangeD(stmp1(0),(stmp1(0)+temp1)+1.0)
anomalies2 = DenseVector.rangeD(stmp2(0),(stmp2(0)+temp2)+1.0)
W_poi = constructGraph(K,pnew,r,theta1,theta2,lambda,rho_tmp,N1,N2)
}
val result=graphAnomalyClass(W_poi,anomalies1,anomalies2)
result
}
def preprocessGraph(adj:DenseMatrix[Double],N1:Int,N2:Int):DenseMatrix[Double]={
val totalUniqueNode=N1.toDouble+N2.toDouble
val totalConnection = sum(adj)
val avgCon=(2.0*totalConnection.toDouble)/totalUniqueNode
val perturbationP = totalConnection / pow(totalUniqueNode,2)
var W = adj + perturbationP // perturbation
var degree = sum(W(*, ::))
var invDeg = pow(degree,-0.5)
var invD = diag(invDeg)
var normW = invD*W*invD
normW
}
####Activity Vector
- compute the singular value decomposition (SVD) and extract the principle singular vector (left singular vector corresponding to the largest singular value)
def getActivity(edge:DenseMatrix[Double]):DenseVector[Double]={
val leftSingular= svd(edge)
var U =leftSingular.U
var Ac1 = abs(U(::,0))
Ac1
}
Activity Vectors in the first window
// perform SVD and get activity vectors for the first 5 graphs
def getFirstActivityVectors(N1:Int,N2:Int,edgeArray:Array[DenseMatrix[Double]],tw:Int):DenseMatrix[Double]={
var winActivity1= DenseMatrix.zeros[Double](N1,tw)
for(i<- 0 to (tw-1)){
var edge_i=edgeArray(i)
var W = preprocessGraph(edge_i,N1,N2)
winActivity1(::,i) := getActivity(W)
}
winActivity1
}
Let’s use MLlib svd rountine next.
// MLlib svd
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Matrix
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.RowMatrix
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.SingularValueDecomposition
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.{IndexedRow, IndexedRowMatrix}
def getSvdSpark(winActivity:DenseMatrix[Double]):DenseVector[Double] = {
val tWinAc1_0 = winActivity.t
val arr = new Array[(Int, Array[Double])](tWinAc1_0.cols)
for(i <- 0 until tWinAc1_0.cols) {
arr(i) = (i, tWinAc1_0(::,i).toArray)
}
val rdd = sc.parallelize(arr)
rdd.cache()
val svd = new IndexedRowMatrix(rdd.map{case(row: Int, colVector: Array[Double]) => {
new IndexedRow(row, new org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.DenseVector(colVector))
}}).computeSVD(5, true, 1e-9)
rdd.unpersist()
val uMatrix = svd.U.rows
val firstCol = DenseVector.zeros[Double](uMatrix.count.toInt)
uMatrix.collect.foreach{row => {
firstCol(row.index.toInt) = row.vector(0)
}}
abs(firstCol)
}
##Generate DCSBM Graphs
// Parameter settings
var graphType:String = "unipartite"
var N1:Int = 900
var N2:Int = N1
var K1:Int = 3
var K2:Int = 3
var s1:Double = N1/K1
var s2:Double = N2/K2
var rho1 = DenseVector.fill(K1){s1/N1}
var rho2 = DenseVector.fill(K2){s2/N2}
var p =DenseVector[Double]{0.05} // within block probability
var r:Double = 0.008 // between block probabilty
var lambda:Double = 0.8 //signal in the graph
val nd: Int = 29 // graph realization sets
var beforeChange:String = "simple"
var changeType:String = "shift" // form, split, shift
val tw =5
// parameter for the powerLaw degree distribution
val beta:Double = 2.5
val xmin:Double = 1
var theta1 = DenseVector.zeros[Double](N1)
var theta2 = DenseVector.zeros[Double](N2)
if(graphType == "unipartite"){
N2 = N1
K2 = K1
theta1 = powerlawRnd(N1,xmin,beta) // generate powerlaw random variable
theta2 = theta1
}else{
theta1 = powerlawRnd(N1,xmin,beta) // type 1 node
theta2 = powerlawRnd(N2,xmin,beta) // type 2 node
}
// generate a dynamic network
val tChange = 20 // at day 21 is the change
var sparseA: Array[DenseMatrix[Double]]=new Array[DenseMatrix[Double]](nd+1)
var anomaly1:DenseVector[Double]=null
var anomaly2:DenseVector[Double]=null
for (m <- 0 to nd){
if(m<tChange && m >tChange){
sparseA(m) = constructGraph(K1,p,r, theta1,theta2,lambda,rho1,N1,N2)
}else{
val G = createA_anomaly(K2, p(0), r, theta1,theta2,lambda,rho2,changeType,graphType)
sparseA(m) = G.W
anomaly1 =G.A1
anomaly2 =G.A2
}
// create graph 1:20 from Dist A
// create graph 21 from Dist B
// create graph 22:30 graph Dist A
}
##Computing node and time scores
// computing node scores and time scores from day 6 onwards
var winAc1_0 = getFirstActivityVectors(N1,N2,sparseA,tw)
var nt = sparseA.length-tw
var timeScore = DenseVector.zeros[Double](nt)
var nodeScore = DenseMatrix.zeros[Double](N1,nt)
for(i <- 0 to nt-1){
var edge_i= sparseA(i+tw)
var W_i = preprocessGraph(edge_i,N1,N2)
var winAc1 = winAc1_0
var refAc1 = getSvdSpark(winAc1) // get reference embedding
var Ac1 = getActivity(W_i) // get current embedding
timeScore(i) = 1 - norm(refAc1.t * Ac1)
var tmp =(Ac1.t * refAc1)* refAc1.t
for(j <- 0 to N1-1){
nodeScore(j,i) = abs((Ac1(j) - tmp.toDenseVector(j)))
}
var winAc_tmp = winAc1_0(::,1 to 4)
winAc1_0 = DenseMatrix.horzcat(winAc_tmp,Ac1.toDenseMatrix.t)
}
##Results
//
import org.apache.spark.sql.types._
import org.apache.spark.sql.DataFrame
def convertScore(matrix:DenseMatrix[Double]):DataFrame={
//val matrix = timeScore.toDenseMatrix
val n = matrix.rows
val m = matrix.cols
val tSb = sc.broadcast(matrix)
// creating schema for DataFrame matrix
val columns = for (i <- 0 until m) yield StructField(s"$i", DoubleType, false)
val indexColumn = Seq(StructField("index", IntegerType, false))
val schema = StructType(indexColumn ++ columns)
val df = sqlContext.createDataFrame(sc.parallelize(0 until n).map { v =>
val values = v +: tSb.value(v,::).t.toArray
Row(values: _*)
}, schema)
df
}
val tScoreDF = convertScore(timeScore.toDenseMatrix)
val nodeScoreDF = convertScore(nodeScore.toDenseMatrix)
tScoreDF.registerTempTable("timeScore_table")
nodeScoreDF.registerTempTable("nodeScore_table")
%r
timedf <- sql(sqlContext, "FROM timeScore_table SELECT *")
timeScore <- collect(timedf)
nodedf <- sql(sqlContext, "FROM nodeScore_table SELECT *")
nodeScore <- collect(nodedf)
%r
display(timeScore)
display(nodeScore)
//%r
/*data.matrix(timeScore, rownames.force = NA)
require(grDevices) # for colours
image(nodeScore)
x<- c(1:25)
timeScore[,2:5]
plot(x,timeScore[,2:26], type="o", xlab="day",
ylab="score" )*/
-
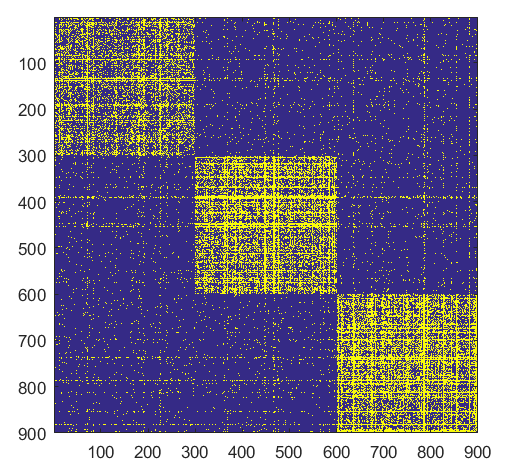
Split
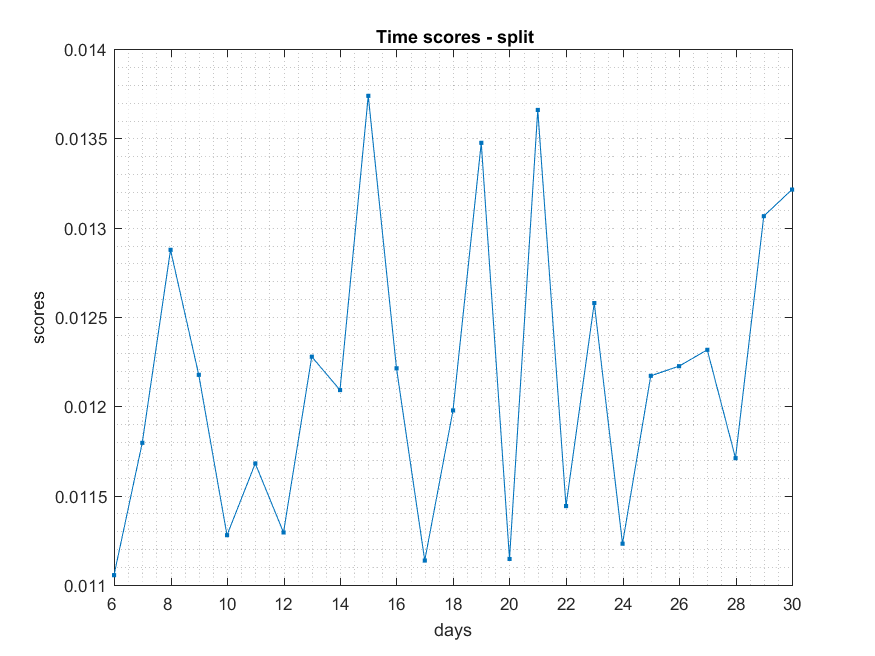
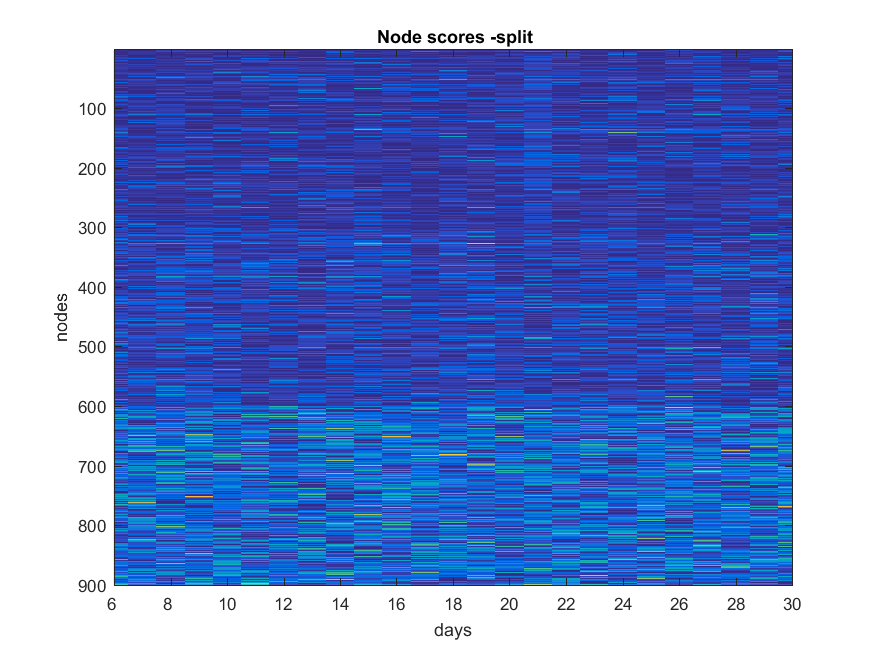
NB: Changed day = 21, changed nodes are from 150-300
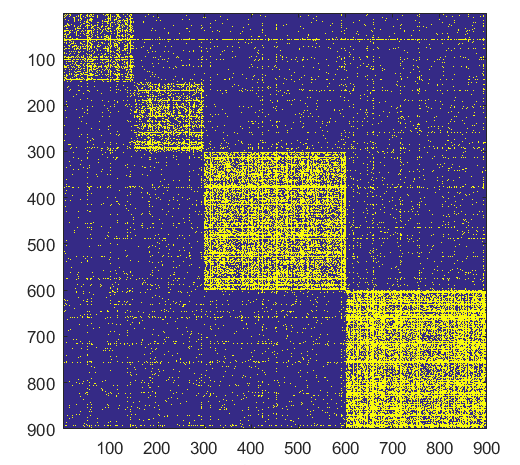
- ###Form
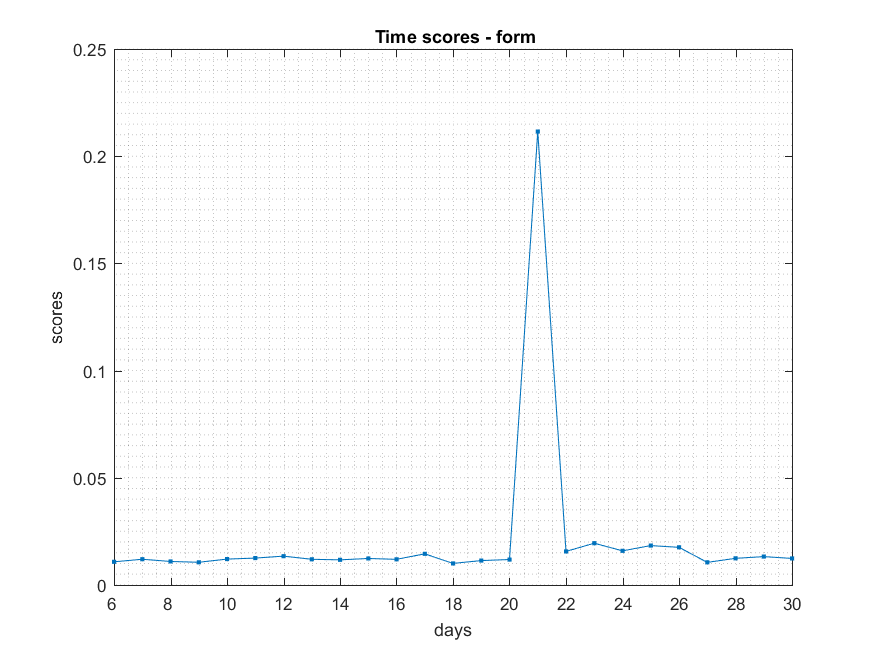
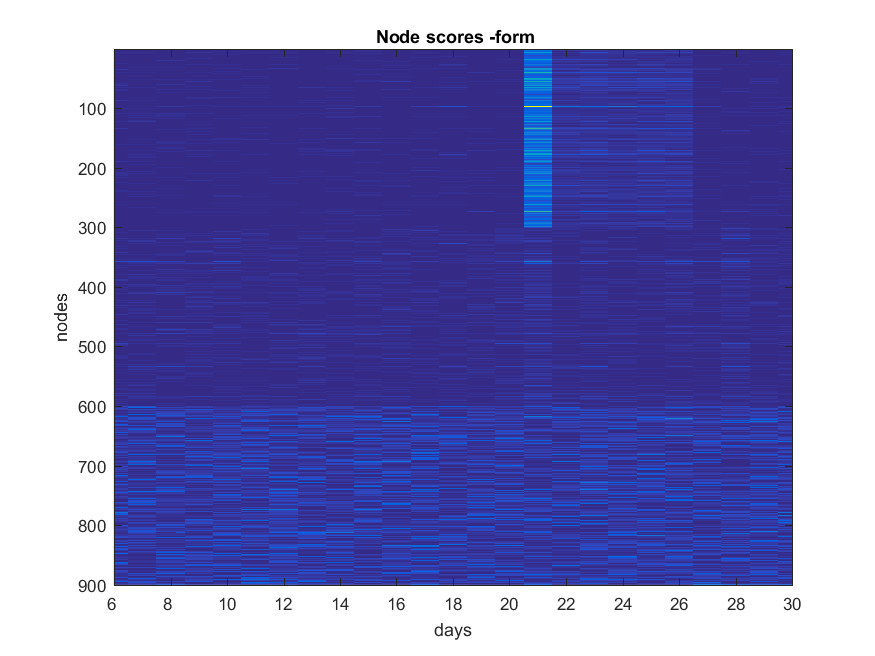
NB: Changed day = 21, changed nodes are from 1-300
- ###Shift
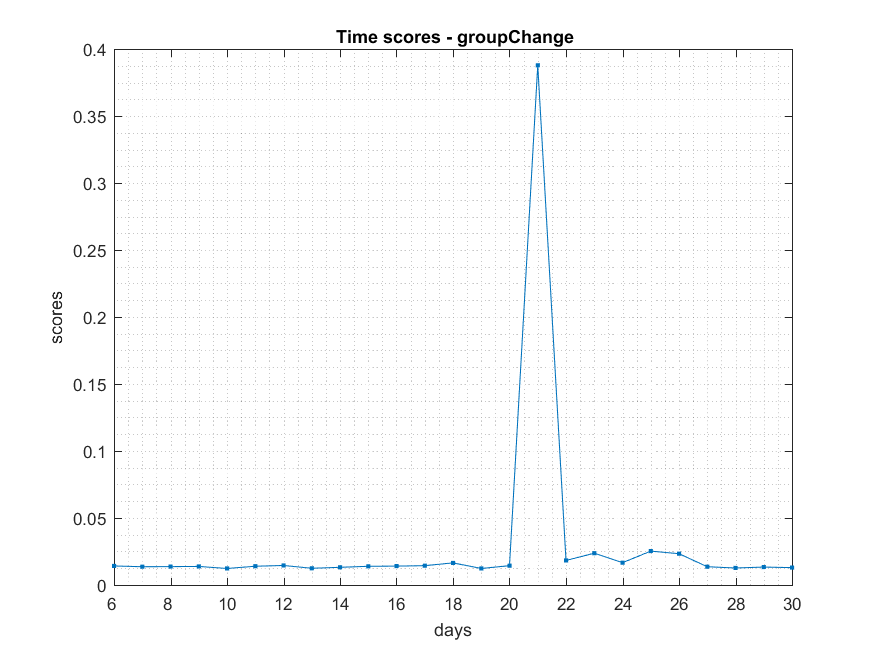
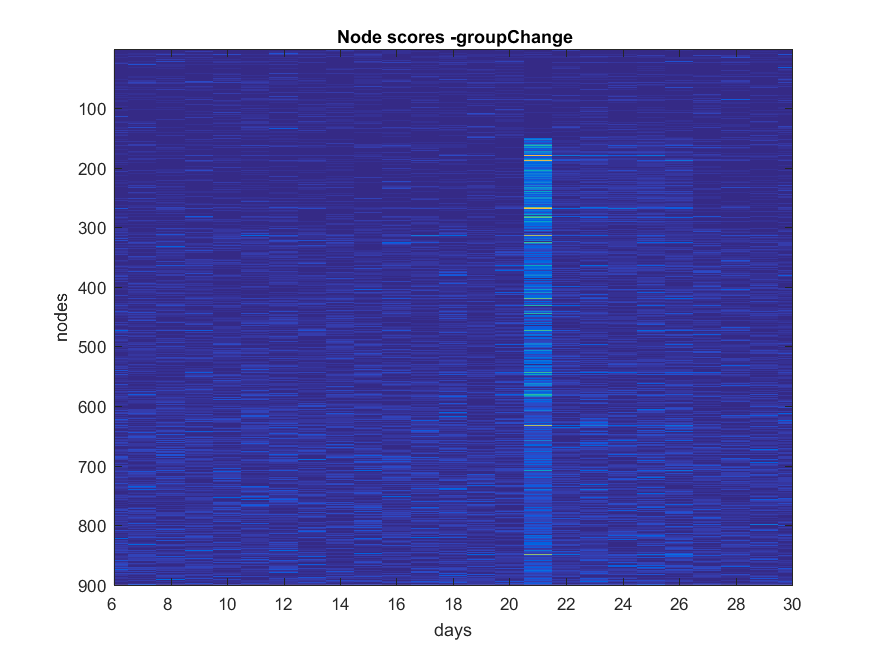
NB: Changed day = 21, changed nodes are from 150-300
##References


